Diffusion and Osmosis - Review
1. Diffusion defined as _____________________________
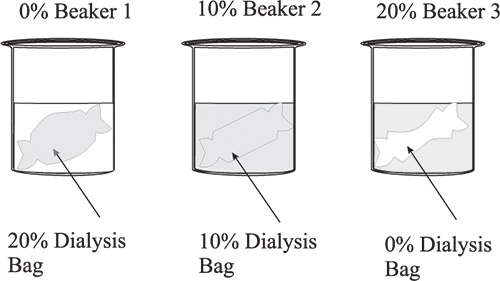
Beaker 1. ___________ Beaker 2. ____________ Beaker 3.____________
3. Diffusion operates in all environments, but Osmosis can only occur across a ___________ .
4. The driving force behind Brownian movement is ______________
5. As the particle of carmine dye diffusion in the liquid, what is the relationship between the size of the particles and amount of movement? _______________
6. Active transport can only occur in _______________________.
7. As a substance diffuses away from its source the rate of diffusion _____________.
In the photo below, the concentrations of potassium permanganate and the associated diffusion are compared.
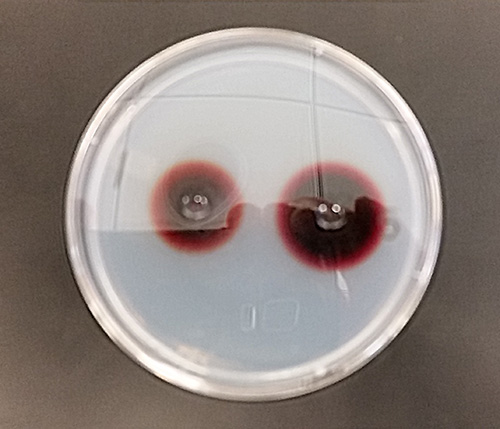
12. The relationship between concentration and rates are diffusion are: ______________________
In the photo below, the molecular weights and rates of diffusion are compared.
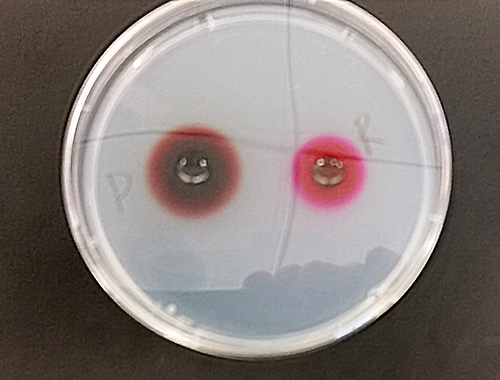
13. The relationship between molecular weights and rates of diffusion are: _______________________
The proces of endocytosis is demonstrated by the Amoeba (below) and a small ciliate.
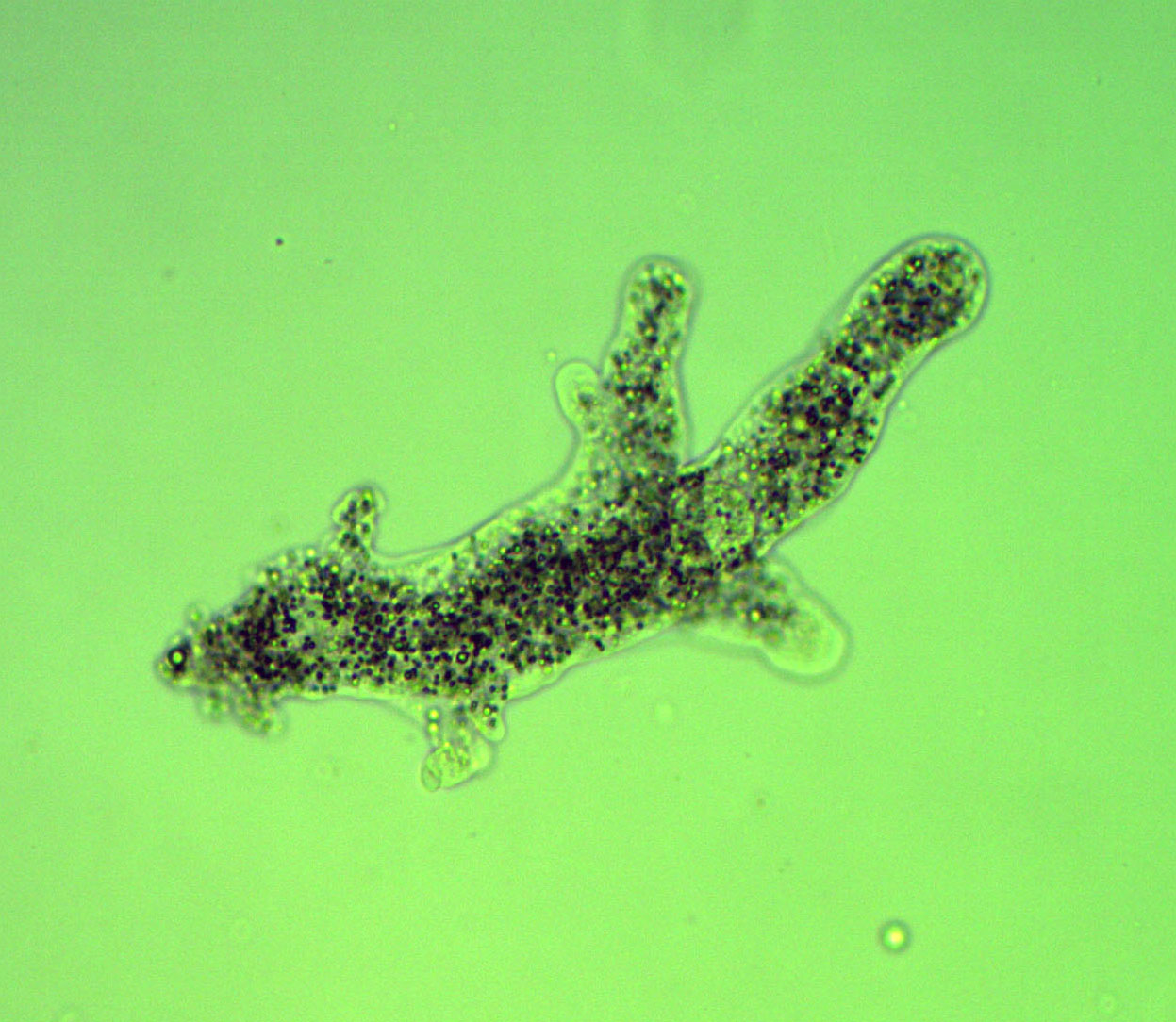
14. How does endocytosis relate to Osmosis, Active Transport and Diffusion? ________________